Vegetal chemistry
|
|
Objectives
Acquire scientific knowledge and skills as well as methodological tools for the sustainable production of biomaterials, biofuels and other biomolecules of substitution. These bioproducts are made from renewable resources through eco-efficient transformation processes (green chemistry).
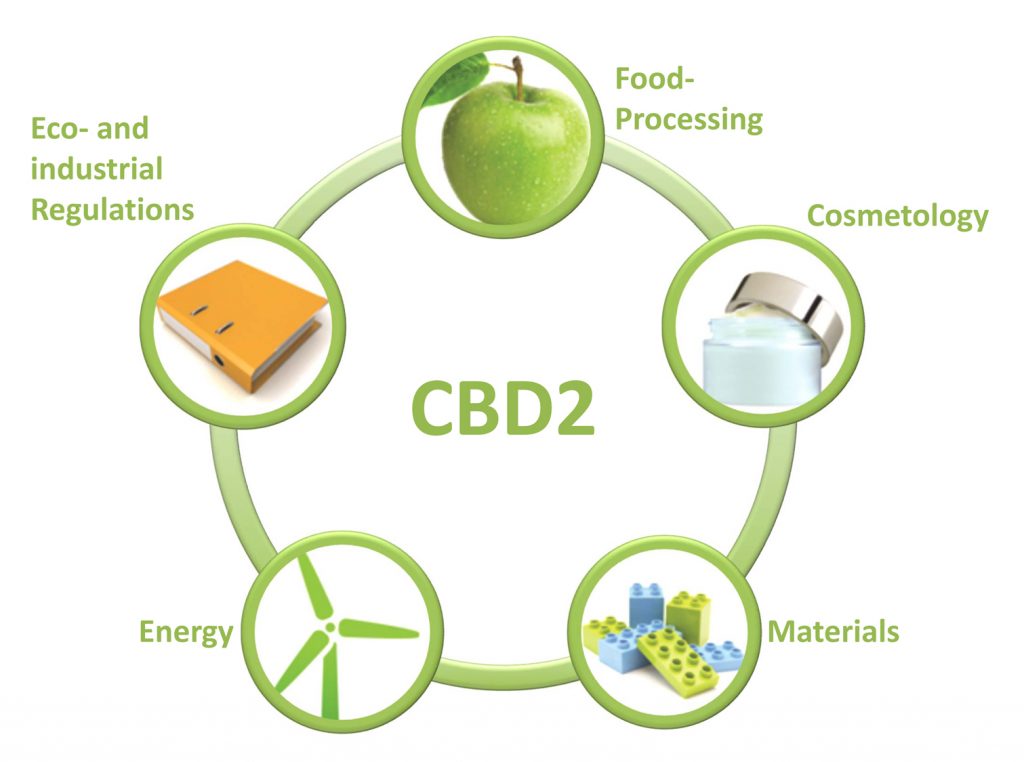
Business sectors
Teaching area
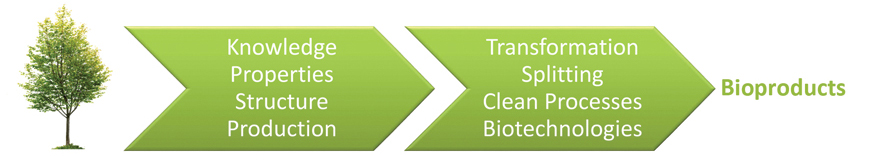
1. Raw material
- Knowledge and control of the raw material
- Selection and improvement of agroresources
- Production: green chemistry and agriculture
2. Bioprocesses
- Technical extraction and separation
- Microbial and enzymatic biotechnology
- «Clean» chemical processes
- Engineering, reactors, modeling
3. Bioproducts
- Biofuels / Energy
- Polymeric biomaterials
- Biomolecules of interest
4. Socio-economic framework
- Regulatory and institutional watch
- Agro-industries: strategy and markets
- Industrial ecology
- Production management and industrial performance
- Analysis of life cycles and eco-assessments
Major project
- Design, sizing and analysis of a sustainable sector for a fixed objective of production of a bioproduct. Students, in groups of 4 or 5, develop a complete sector (from the resource to the bioproduct) answering the different issues of a green and sustainable chemistry. The students rely on bibliographical resources, exchanges with academic researchers and industrialists likely to be interested in the sector.
Jobs and job area targetted
The Research and Development (R&D) engineer pilots
the scientific aspects of innovative projects in a laboratory.
He is the essential interface between the design and the development of new
products. He follows the evolution of the project from the laboratory to the pilot scale.
The environmental engineer is responsible for defining and implementing,
both operationally and administratively, an environmental management system
aimed at reducing the environmental impacts within its structure: water and energy consumption, identification of pollutant gas emissions, environmental risk analysis, integration of eco-design into processes.
The project manager plans, organizes and coordinates a project
from the design to completion. Projects can be in research
and development, in production or reorganization of systems.
The business engineer realizes the assembly, the control and the follow-up
of a commercial case associating the technical and financial aspects.
He identifies the needs of the customer and offers a suitable product.
The production engineer manages a production workshop.
He follows and plans production and supervises the teams of operators.
He coordinates the launch of new products.
It ensures the proper functioning of the production tool.